Anatomy of a Diamond
The structure of a diamond
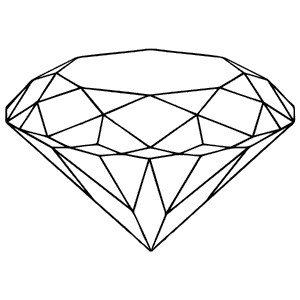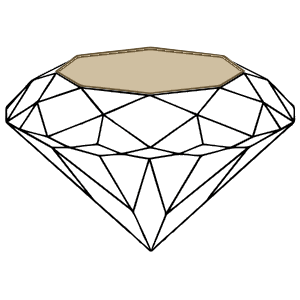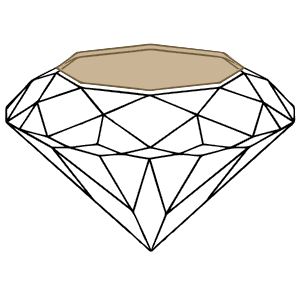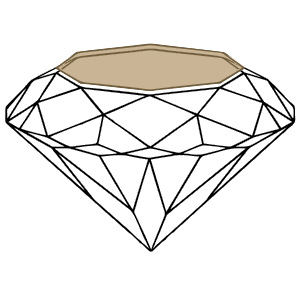
Table
Table is the largest facet of a diamond. It resembles a tabletop hence the name. Due to its coverage and significant position the area plays a major part in the reflecting light that falls upon the gem. The table should align parallelly with the girdle for the perfect symmetry of the diamond.
Crown
Crown is the portion that covers the space between the table and the girdle. The slanting portion determines the shine of the diamond to an extent for this part is quite important and contributes a lot to the reflection of light. Crown is defined either with step cut facets or brilliant cut facets. Brilliant cut come with more facets than step cuts. Hence, the diamonds with the former sparkle more than with the latter.
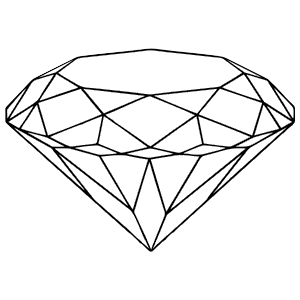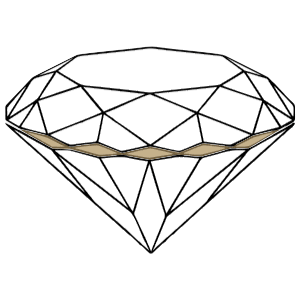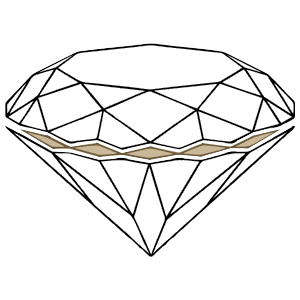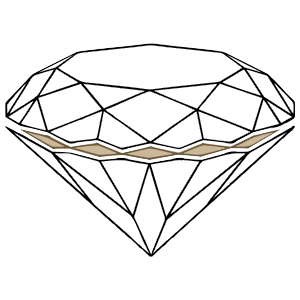
Girdle
The girdle is where the crown and the pavilion meet and hence, it is the widest part of a diamond. Being an area that does not take much space, one often fails to notice girdles like other diamond parts. A girdle can have facets or be smooth or rough in texture.
Pavilion
The pavilion is the area that falls between the culet and the girdle. Like the crown, this area is also slanting in nature. As a pavilion plays a major role in determining the shine, the way a pavilion is crafted matters a lot in the quality of a diamond.
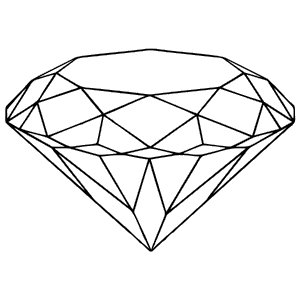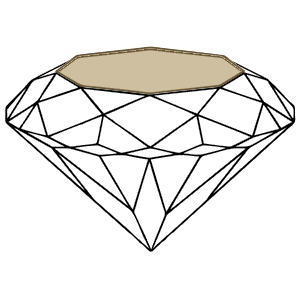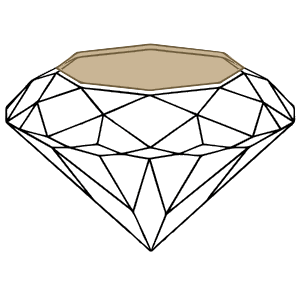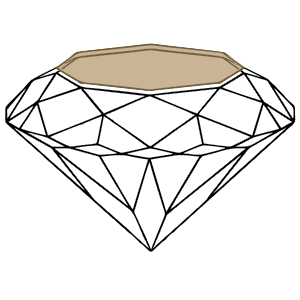

Culet
The pointed tip is the culet. Culets tend to be sharper with the newer cuts like the brilliant cut. The sharper the culet is, the better the finish will be. However, sharp culets can easily get chipped. Diamonds with sharp culets are thereof handled with care.
Depth
The depth of the diamond is the length from the table to the tip of the culet. In simple terms, it is the height of a diamond. The depth of the diamond impacts the light reflection. A diamond with shallow depth and a broader body will let the light pass through it thereby not giving the optimal reflection.

More to Know
Apart from the above mentioned, there are other certain terms that are also essential in knowing the anatomy of a diamond.
Table percentage
The table percentage is the area of the table in proportion to the diameter of the diamond. The diameter would be the size of the girdle as it is the widest point of a diamond. A tall crown will give a smaller percentage denoting a round appearance. A shorter crown on the other hand gives a higher table percentage denoting a flattened appearance.
Pavilion angle
It is the average of all angles of the pavilion facets and the girdle. The ideal pavilion angle will fall between 40.6 and 41.8 degrees giving the apt amount of light reflection.
Crown height
The width of the crown determines the amount of shine of the diamond as the crown is one of the most visible parts.
Crown angle
The angle formed where the girdle meets the bezel facets. 31.5 to 36.5 degrees should be the optimal crown angle for the light to be dispersed perfectly.
Girdle thickness
The girdle thickness hugely impacts the structure of a diamond. A highly thick girdle can be a burden for the diamond due to the added weight whereas the girdle being too thin can lead to the gen having a sharp edge that is prone to chipping. Girdle thickness is an aspect that is given extra focus in manufacturing a diamond.
Lower Girdle
This is the percentage of the length of the lower girdle facets in comparison to the depth of the pavilion. The ratio of a perfectly cut diamond would range between 65 to 90.
Conclusion
Each aspect by itself will not make much sense. It is the right combination of all that gives a diamond the value and quality that posses. The symmetry of a diamond therefore highly depends on all the aspects that were discussed in the article. A slight variation from the optimal measurements can lead to imperfections. A perfectly cut diamond will therefore be the gem that can entice anyone with its shine that happens as a result of all the details.




